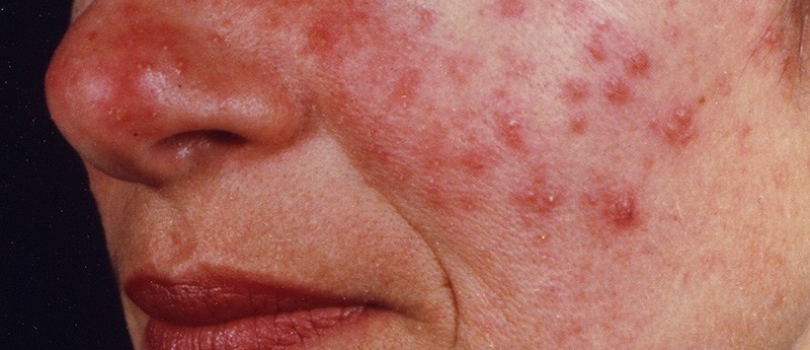
Roza Disease
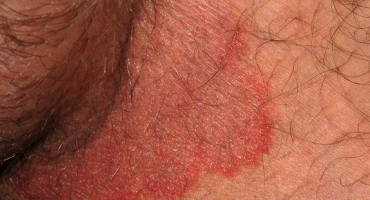
The nose, chin, forehead and cheeks, especially the face of the middle part of the face, starting with redness and burning attacks, then the acne, permanent redness, increased capillaries, skin edema and swelling is a chronic skin disease that causes appearance. It is also known as Roza disease, rose disease and laughing.
Causes of Roza disease?
Although the cause of Roza disease is not known exactly; among the accused factors;
1. Genetic predisposition.
2. Infectious causes: The most accused infectious agents are the Helicobacter pylori (H pylori) bacteria in the stomach and the demodex mites in the percentage.
3. Environmental factors: Numerous environmental factors such as ultraviolet light and surrounding heat changes play a role in the initiation or exacerbation of rosaceous lesions.
4. Psychogenic factors: Especially intermittent burning and redness attacks can be affected by changes in the patient's mood and psychological stress.
5. Natural immune system: In recent years, the imbalance in the natural defense system of the skin is mentioned.
What are the causes of Roza disease?
Foods and drinks (hot and cold drinks with foods soup, tea / coffee, spicy foods, bitter, pickles, chocolate, alcohol ...)
Weather conditions (sunlight, hot weather, cold weather, humidity, wind)
Psychological stress and excessive exercise
Bathroom, cleaning and personal care products (Hot bath and face irritant cleaning materials, cologne, tonic, rose water, wet wipes)
Medications (Long-term topical corticosteroid use)
Systemic conditions (premenstrual, pregnancy, menopause, severe cough and constipation)
How is Rosacea's disease treated?
BBL Laer Treatment: BBL laser treatment is the most effective, comfortable and safe treatment for rosacea. BBL Laser treatment is a painless, painless and needle-free method.
Although it is difficult to resolve the root of the disease, it is possible to keep under control with treatment.
General precautions: Most importantly, you should avoid the factors that increase the symptoms of the disease.
Sun protection: One of the most important factors triggering the disease is the sun. You should use a suitable sunscreen recommended by your dermatologist at intervals of 2-4 hours per day. Avoid sun exposure during sunlight.
Topical treatment: Usually cream and gels are used in mild cases. The most commonly used metronidazole (cream, gel, lotion), azelaic acid (cream, gel) and sodium sulfacetamide, sulfacetamide + sulfur. Other drugs include tretinoin, benzoyl peroxide, erythromycin, clindamycin, tetracycline, 5% permethrin cream, tacrolimus and pimecrolimus.
Systemic Treatment: In severe cases, systemic treatment is applied alone or in combination with topical agents. The most commonly preferred systemic agents are systemic antibiotics (minocycline, doxycycline, tetracycline, metronidazole and azithromycin) and isotretinoin, a product of vitamin A.
Is there a special diet for Roza?
Although you do not have a special diet for Roza disease, you should stay away from food and beverages that increase redness. You should also avoid smoking and other tobacco products.









.png)